Understanding Carbon Credits Price Per Ton: A Comprehensive Guide
Carbon credits, also known as carbon offsets, have become a crucial component in the global effort to combat climate change. These credits represent the right to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. The price of carbon credits per ton can vary widely, influenced by several factors. Let’s delve into the details to understand what determines the carbon credits price per ton.
Market Dynamics

The price of carbon credits is primarily driven by market dynamics. These dynamics include the supply and demand for credits, as well as regulatory policies and international agreements.
Supply and demand: The availability of carbon credits is influenced by the number of projects that generate them. These projects can range from renewable energy installations to reforestation efforts. When the supply of credits increases, the price tends to decrease, and vice versa. Similarly, if there is high demand for credits, the price will likely rise.
Regulatory policies: Government regulations play a significant role in determining the price of carbon credits. For instance, countries with stringent carbon emission targets may have higher carbon prices. Additionally, policies that incentivize the reduction of emissions can also impact the price of carbon credits.
International agreements: International agreements like the Paris Agreement have set global targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These agreements can influence the price of carbon credits by creating a unified framework for carbon trading.
Geographical Factors

The geographical location of carbon credit projects can also affect their price. Here are a few key factors:
Project type: Different types of projects generate carbon credits at varying rates. For example, a wind farm may generate more credits per ton of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) than a solar farm. The type of project can influence the price of carbon credits.
Location: The geographical location of a project can impact its cost and, consequently, the price of its carbon credits. Projects in regions with lower labor and operational costs may offer cheaper credits.
Market access: The ease of accessing the carbon credit market can also affect prices. Projects in regions with well-established carbon markets may have higher prices due to greater liquidity and demand.
Project Quality and Verification
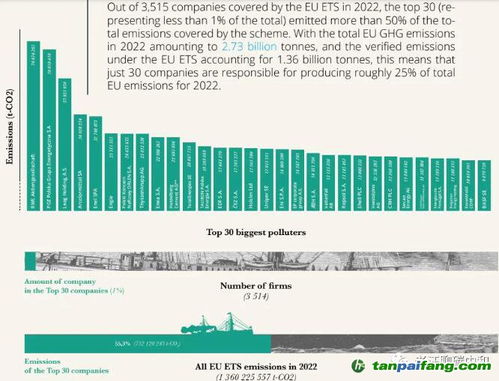
The quality and verification of carbon credit projects are critical factors in determining their price. Here’s why:
Project quality: High-quality projects are more likely to generate a higher price for their carbon credits. This is because they are more likely to be accepted by buyers who are looking for reliable and effective ways to reduce their carbon footprint.
Verification: Carbon credit projects must undergo verification to ensure that they meet certain standards. Projects with a strong track record of verification are more likely to command higher prices.
Historical Price Trends
Understanding the historical price trends of carbon credits can provide valuable insights into future price movements. Here’s a brief overview:
2005-2010: During this period, carbon credit prices were relatively stable, ranging from $10 to $30 per ton of CO2e.
2011-2014: The price of carbon credits experienced a significant increase, reaching a peak of around $20 per ton of CO2e in 2013.
2015-2020: The price of carbon credits has been relatively stable, hovering around $10 to $15 per ton of CO2e.
Table: Historical Carbon Credit Prices
| Year | Carbon Credit Price (per ton of CO2e) |
|---|---|
| 2005-2010 | $10 – $30 |
| 2011-2014 | $15 – $20 |
| 2015-2020 | $10 – $15 |
Conclusion
Understanding the carbon credits price per ton requires considering various factors, including market dynamics, geographical location, project quality, and historical price trends. By analyzing these factors, you can gain a better understanding of the factors that influence carbon credit prices and make informed decisions when purchasing or selling carbon credits.