Polyscope Tone Mapping Parameters: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the intricacies of tone mapping parameters in Polyscope is essential for anyone looking to enhance the visual quality of their 3D renderings. Tone mapping is a technique used to convert the luminance range of high-dynamic-range (HDR) images to a range that can be displayed on standard monitors or screens. By doing so, it allows for a more realistic representation of lighting and color in the final output. In this article, we will delve into the various tone mapping parameters available in Polyscope, explaining their functions and how they can be adjusted to achieve the desired visual outcome.
Understanding Tone Mapping

Tone mapping is a crucial step in the post-processing pipeline of HDR images. It helps to bridge the gap between the vast luminance range of HDR content and the limited range of standard displays. Polyscope offers a range of tone mapping parameters that can be adjusted to achieve the best possible results. Before diving into the specific parameters, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how tone mapping works.
In simple terms, tone mapping reduces the contrast of an HDR image to fit the display’s capabilities. This process involves mapping the luminance values of the HDR image to a new range that is suitable for the display. The goal is to preserve as much detail as possible while ensuring that the image remains visually pleasing.
Polyscope Tone Mapping Parameters
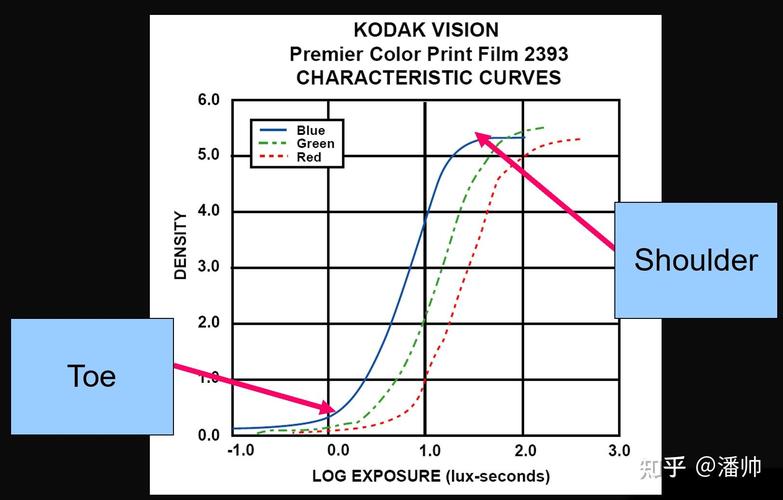
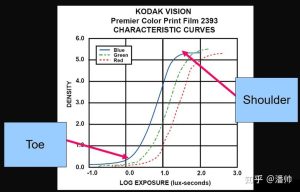
Polyscope provides a variety of tone mapping parameters that can be adjusted to suit your specific needs. Here’s a detailed look at each of these parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Exposure | Adjusts the overall brightness of the image. A higher value increases the brightness, while a lower value decreases it. | 1.0 |
| Contrast | Controls the contrast of the image. Increasing the contrast enhances the difference between light and dark areas, while decreasing it softens the image. | 1.0 |
| Gamma | Adjusts the gamma curve of the image. This parameter affects the perceived brightness of different areas in the image. | 2.2 |
| White Point | Changes the color temperature of the image. A higher value produces a cooler, bluer image, while a lower value results in a warmer, redder image. | 6500K |
| Black Point | Adjusts the luminance of the darkest areas in the image. Increasing the black point value makes the image darker, while decreasing it makes it brighter. | 0.0 |
| Highlight Compression | Controls the compression of the brightest areas in the image. A higher value reduces the contrast in the highlights, while a lower value preserves more detail. | 0.5 |
| Shadow Compression | Adjusts the compression of the darkest areas in the image. A higher value reduces the contrast in the shadows, while a lower value preserves more detail. | 0.5 |
By adjusting these parameters, you can fine-tune the visual appearance of your HDR images to suit your specific requirements. Let’s take a closer look at each parameter and its impact on the final output.
Exposure

The exposure parameter is responsible for adjusting the overall brightness of the image. A higher exposure value increases the brightness, making the image appear lighter. Conversely, a lower exposure value decreases the brightness, resulting in a darker image. Finding the right exposure level is crucial for achieving a balanced and visually appealing image.
Contrast
The contrast parameter controls the difference between light and dark areas in the image. Increasing the contrast enhances the distinction between these areas, resulting in a more vibrant and dynamic image. On the other hand, decreasing the contrast softens the image, reducing the sharpness of light and dark transitions. Adjusting the contrast can help you achieve the desired level of detail and depth in