What is Tone Deaf?
Tone deafness, also known as amusia, is a condition where an individual is unable to recognize or distinguish between different musical pitches. It is a fascinating topic that has intrigued scientists and musicians alike. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of tone deafness, including its causes, symptoms, and the impact it has on individuals’ lives.
Understanding Tone Deafness
Tone deafness is a congenital condition, meaning it is present from birth. It is estimated that around 4% of the population is tone deaf. While some individuals may have a mild form of tone deafness, others may struggle significantly with musical tasks that require pitch recognition.
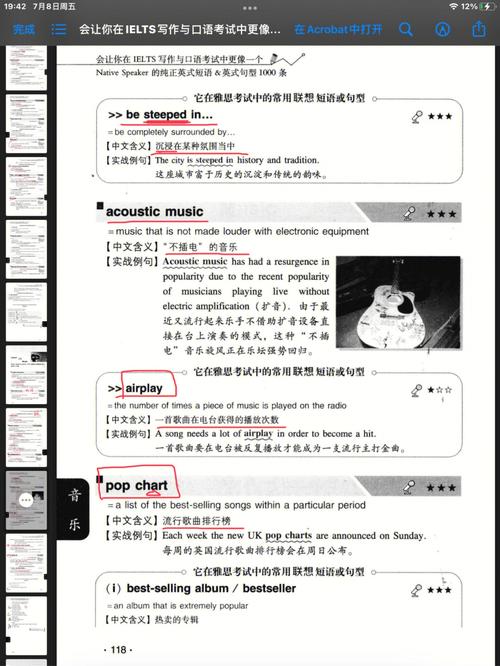
One of the key characteristics of tone deafness is the inability to match a heard pitch with a sung or played pitch. This can make it challenging for tone deaf individuals to sing in tune or play an instrument. However, it is important to note that tone deafness does not affect one’s ability to appreciate music or enjoy listening to it.
Causes of Tone Deafness
The exact cause of tone deafness is still not fully understood, but researchers have identified several factors that may contribute to its development.
-
Genetic Factors: Studies have shown that tone deafness can be inherited, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.
-
Developmental Factors: Some researchers believe that tone deafness may be related to the development of the auditory system during early childhood.

-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to musical training or instruction may play a role in the development of tone deafness.
Symptoms of Tone Deafness
There are several symptoms that can indicate tone deafness. These include:
-
Inability to match pitches: Tone deaf individuals may struggle to sing or play a musical instrument in tune.
-
Difficulty with rhythm: Some tone deaf individuals may also have difficulty with rhythm and timing.
-
Perceptual difficulties: Tone deaf individuals may have difficulty distinguishing between similar musical pitches or identifying the key of a piece of music.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of tone deafness on an individual’s life can vary widely. Some individuals may experience minimal challenges, while others may find it significantly affects their daily activities.
For example, tone deaf individuals may struggle with tasks such as singing in a choir, playing an instrument, or even participating in musical games. However, many tone deaf individuals are able to lead fulfilling lives and pursue their interests in other areas.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing tone deafness typically involves a series of tests that assess an individual’s ability to recognize and match musical pitches. These tests may include singing exercises, listening tasks, and playing musical instruments.
While there is no cure for tone deafness, there are several strategies that can help individuals manage their condition. These include:
-
Music therapy: Music therapy can help tone deaf individuals develop their musical skills and improve their ability to recognize and match pitches.
-
Technological aids: Some individuals may find it helpful to use technological aids, such as pitch correction software or apps, to improve their musical abilities.
-
Support groups: Joining a support group can provide individuals with the opportunity to connect with others who share similar experiences and offer mutual support.
Conclusion
Tone deafness is a fascinating and complex condition that affects a significant number of individuals. While it can present challenges, there are various strategies and resources available to help individuals manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and impact of tone deafness, we can better support and empower those who are affected by this condition.