Which Statement Should Be Revised for a More Formal Tone?
When crafting formal documents, such as business reports, academic papers, or legal briefs, the choice of words and sentence structure is crucial. One key aspect to consider is the revision of statements to enhance their formality. This article will delve into various dimensions to help you identify which statements should be revised for a more formal tone.
Understanding Formal Tone
Before we proceed, it’s essential to understand what constitutes a formal tone. A formal tone is characterized by precision, objectivity, and professionalism. It avoids colloquialisms, contractions, and overly casual language. Here are some key elements to consider when assessing the formality of a statement:

- Precision: Use specific and clear language to convey your message.
- Objectivity: Maintain an unbiased perspective and avoid personal opinions.
- Professionalism: Use formal language and sentence structures that reflect the seriousness of the subject matter.
Now, let’s explore some common scenarios where statements may require revision for a more formal tone.
1. Avoiding Colloquialisms
Colloquialisms are informal expressions that are commonly used in everyday conversation. In formal writing, it’s best to avoid these expressions to maintain a professional tone. For example:
| Informal Statement | Formal Revision |
|---|---|
| “I was just wondering if you could help me out with this project?” | “I am seeking your assistance with this project.” |
| “I think this idea is kind of cool.” | “This idea appears to be innovative and merits further consideration.” |
2. Eliminating Contractions
Contractions, such as “can’t,” “won’t,” and “shouldn’t,” are informal and should be avoided in formal writing. Replace contractions with their full forms to maintain a formal tone. For example:
| Informal Statement | Formal Revision |
|---|---|
| “I can’t finish this report on time.” | “I am unable to complete this report within the specified timeframe.” |
| “She won’t agree with this decision.” | “It is unlikely that she will concur with this decision.” |
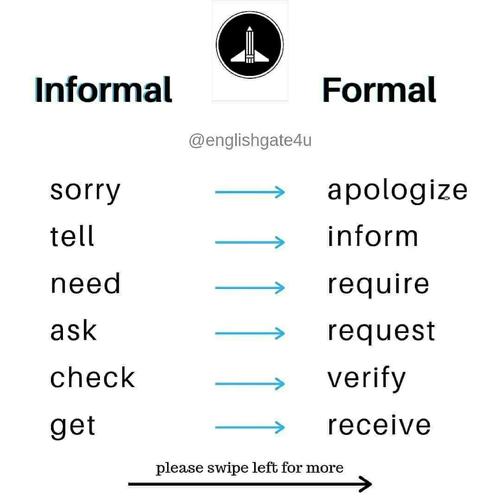
3. Using Appropriate Language
Choose words that are appropriate for the subject matter and audience. Avoid slang, jargon, and overly casual language. For example:
| Informal Statement | Formal Revision |
|---|---|
| “I’m not sure if this is the right approach.” | “It is uncertain whether this approach is the most suitable.” |
| “This is a no-brainer.” | “This decision is straightforward and does not require extensive analysis.” |
4. Refining Sentence Structure
Formal writing often requires a more complex sentence structure. Use compound and complex sentences to convey your message effectively. For example:
| Informal Statement | Formal Revision |
|---|---|
| “I went to the store and bought some milk.” | “Upon visiting the store, I procured a supply of milk.” |
| “He’s really good at playing basketball.” | “He possesses exceptional skills in basketball.” |
5. Avoiding Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns, such as “I,” “you,”