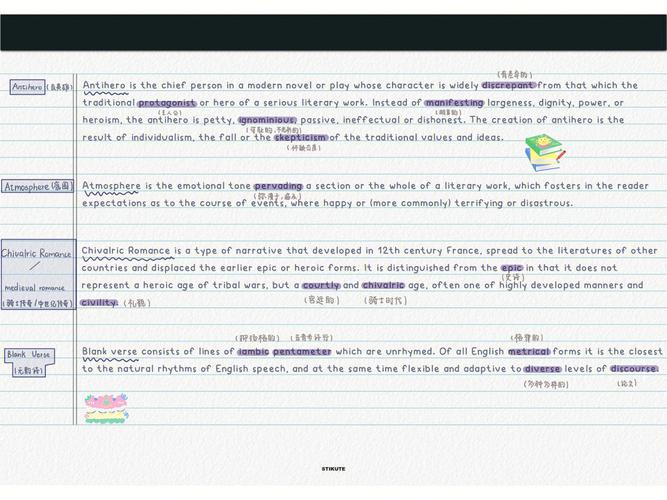
Literary Examples of Tone
Understanding the tone of a literary work is crucial to fully appreciating its depth and impact. Tone refers to the attitude or feeling conveyed by the author through the words and style of the writing. It can range from serious and solemn to humorous and light-hearted. In this detailed exploration, we will delve into various literary examples that showcase different tones, helping you grasp the nuances of this essential literary element.
Formal and Serious Tone
One of the most common tones in literature is formal and serious. This tone is often found in historical novels, biographies, and serious non-fiction works. It is characterized by a formal language, precise diction, and a focus on the subject matter. For instance, in “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee, the tone is formal and serious, reflecting the gravity of the issues discussed, such as racial injustice and moral growth.
| Character | Example |
|---|---|
| Atticus Finch | “You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view… Until you climb inside of his skin and walk around in it.” |
| Jem Finch | “I wish I had never seen the inside of that courthouse.” |
Humorous and Light-hearted Tone
On the opposite end of the spectrum, we have the humorous and light-hearted tone. This tone is often found in comedies, satires, and fantasy novels. It is characterized by a playful language, witty dialogue, and a focus on entertainment. A prime example is “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald, where the tone is humorous and light-hearted, despite the underlying themes of the American Dream and social decay.
“Can you picture me and Gatsby sitting on a couch laughing?”
“Can you picture me and Gatsby sitting on a couch laughing?”
Ironical and Satirical Tone
Irony and satire are powerful tools in literature, allowing authors to convey their opinions and criticism of society. An ironic and satirical tone is often found in works like “Animal Farm” by George Orwell and “Brave New World” by Aldous Huxley. These works use irony and satire to expose the flaws and absurdities of their respective societies.
Example: “Animal Farm” by George Orwell
In “Animal Farm,” Orwell employs irony and satire to criticize the Soviet Union and the Russian Revolution. The farm animals, representing the different classes of society, rise up against their oppressive human masters and establish their own government. However, as time passes, the animals’ leaders, Napoleon and Snowball, become increasingly corrupt and resemble the very humans they overthrew.
Example: “Brave New World” by Aldous Huxley
In “Brave New World,” Huxley uses irony and satire to critique the dystopian society of the future. The citizens of this world are genetically engineered and conditioned to be content with their lives, which are devoid of individuality and creativity. The tone is both ironic and satirical, as the characters struggle to find meaning and purpose in their lives.
Reflective and Sentimental Tone
A reflective and sentimental tone is often found in poetry, personal essays, and memoirs. This tone is characterized by a focus on emotions, memories, and personal experiences. For example, in “The Road Not Taken” by Robert Frost, the tone is reflective and sentimental, as the speaker contemplates the choices made in life and the paths not taken.
“Two roads diverged in a yellow wood, and sorry I could not travel bothAnd be one traveler, long I stoodAnd looked down one as far as I couldTo where it bent in the undergrowth;”
Conclusion
Understanding the tone of a literary work is essential for appreciating its full impact. By examining various literary examples, we can see how tone can range from formal and serious to humorous and light-hearted, ironic and satirical, and reflective and sentimental. By recognizing these different tones, we can gain a deeper understanding of the author’s intentions and the message they wish to convey.