What is a Tone in Literature?
A tone in literature refers to the overall mood or atmosphere that a writer creates through their choice of words, sentence structure, and narrative style. It is an essential element that can greatly influence how readers perceive and interpret a piece of writing. Understanding the tone of a literary work is crucial for appreciating its full impact and depth. Let’s delve into the various dimensions of tone in literature.
Defining Tone
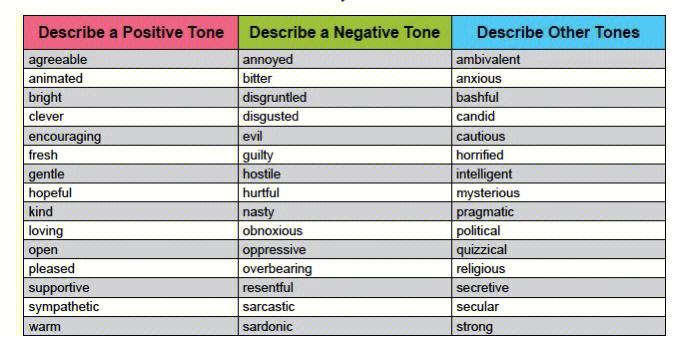
The tone of a literary work can be described as the writer’s attitude or emotional response towards the subject matter. It is the emotional essence of the writing that resonates with the reader. Tone can be light-hearted, serious, solemn, humorous, or any other emotional state that the writer wishes to convey.
Types of Tone

There are several types of tone that can be identified in literature:
| Type of Tone | Description |
|---|---|
| Humorous | Creates a light-hearted and amusing atmosphere, often through the use of irony, sarcasm, or wit. |
| Serious | Conveys a sense of gravity and importance, often dealing with serious themes or issues. |
| Solemn | Evokes a sense of reverence or solemnity, often associated with religious or moral themes. |
| Tragic | Depicts a sense of sorrow, despair, or loss, often resulting in a melancholic atmosphere. |
| Ironical | Conveys a sense of contradiction or incongruity, often used to highlight the absurdity or injustice of a situation. |
Creating Tone

Writers employ various techniques to create a specific tone in their work:
-
Word Choice: The selection of words can greatly influence the tone. For example, using words like “serene” or “melancholic” can evoke a calm or sad atmosphere, respectively.
-
Sentence Structure: The length and complexity of sentences can contribute to the overall tone. Short, simple sentences can create a sense of urgency or excitement, while longer, more complex sentences can convey a sense of depth or introspection.
-
Descriptive Language: The use of vivid and evocative descriptions can help set the tone. For instance, describing a stormy night can create a sense of tension and suspense.
-
Characterization: The way characters are portrayed can also contribute to the tone. A character’s actions, thoughts, and dialogue can all help establish the mood of the story.
Importance of Tone
The tone of a literary work plays a significant role in shaping the reader’s experience. Here are a few reasons why tone is important:
-
Emotional Connection: A well-crafted tone can evoke emotions in the reader, allowing them to connect with the characters and the story on a deeper level.
-
Understanding Themes: The tone can help readers grasp the underlying themes and messages of the work. For example, a humorous tone might be used to address serious issues in a light-hearted manner.
-
Appreciating Style: The tone can also showcase the writer’s unique style and voice. A writer’s choice of tone can reveal their perspective and artistic vision.
Examples of Tone in Literature
Here are a few examples of how tone is used in literature:
-
In “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee, the tone is primarily serious and solemn, reflecting the gravity of the racial injustice and moral dilemmas faced by the characters.
-
In “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald, the tone is both tragic and ironic, highlighting the emptiness and disillusionment of the American Dream.
-
In “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen, the tone is humorous and light-hearted, showcasing the wit and social commentary of the era.
Understanding