Writing Tones: A Comprehensive Guide for Effective Communication
Understanding the different writing tones is crucial for effective communication. Whether you are writing a business report, a personal letter, or a creative piece, the tone you choose can greatly impact how your message is received. In this article, we will delve into various writing tones, their characteristics, and when to use them.
Formal Tone

The formal tone is characterized by a professional and respectful manner. It is often used in business, academic, and legal writing. Here are some key features of a formal tone:
- Use of formal language and vocabulary
- Objective and factual presentation of information
- Formal salutations and closings
For example, in a business report, you might write: “The financial results for the quarter were as follows: revenue increased by 10%, and expenses decreased by 5%.”
Informal Tone
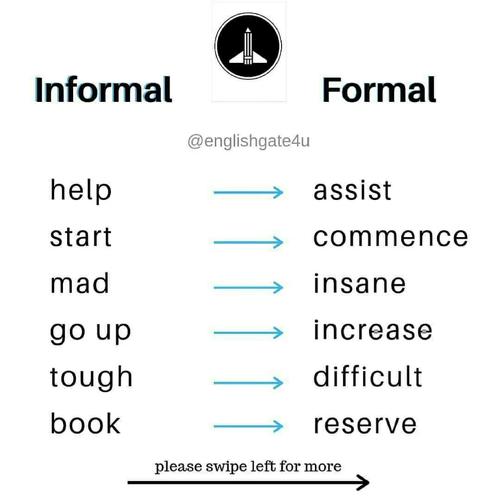
The informal tone is more relaxed and conversational. It is commonly used in personal correspondence, social media, and casual writing. Here are some features of an informal tone:
- Use of colloquial language and slang
- Personal and subjective expression
- Informal salutations and closings
For instance, in a text message to a friend, you might say: “Hey, I’m so excited about the party this weekend! I can’t wait to see you!”
Objective Tone
The objective tone aims to present information without bias or personal opinion. It is often used in scientific, technical, and academic writing. Here are some characteristics of an objective tone:
- Use of neutral language and vocabulary
- Focus on facts and evidence
- Clear and concise presentation of information
For example, in a research paper, you might write: “The study found that the new medication significantly reduced symptoms in patients with chronic pain.”
Subjective Tone
The subjective tone expresses personal opinions, feelings, and experiences. It is commonly used in creative writing, personal essays, and opinion pieces. Here are some features of a subjective tone:
- Use of expressive language and vivid imagery
- Personal anecdotes and reflections
- Emotional and persuasive language
For instance, in a personal essay, you might write: “Looking back on my childhood, I realize how much my parents’ love and support shaped my character.”
Descriptive Tone
The descriptive tone aims to create a vivid picture of a person, place, or event. It is often used in creative writing, travel writing, and descriptive essays. Here are some characteristics of a descriptive tone:
- Use of sensory details and descriptive language
- Focus on the appearance, sounds, and emotions of the subject
- Engaging and immersive narrative
For example, in a travel blog, you might write: “The sun set over the horizon, casting a golden glow over the tranquil beach. The sound of waves crashing against the shore filled the air, creating a sense of peace and relaxation.”
Expository Tone
The expository tone explains and informs the reader about a topic. It is commonly used in informative articles, how-to guides, and educational materials. Here are some features of an expository tone:
- Use of clear and logical organization
- Objective and factual presentation of information
- Use of headings, subheadings, and bullet points for easy readability
For instance, in a how-to guide, you might write: “To bake a perfect cake, follow these steps: 1. Preheat the oven to 350掳F. 2. Grease and flour the cake pan. 3. Mix the ingredients together and pour into the pan. 4. Bake for 30-35 minutes.”
Argumentative Tone
The argumentative tone presents a viewpoint and supports it with evidence and reasoning. It is commonly used in persuasive essays, opinion pieces, and debate. Here are some characteristics of an argumentative tone:
- Use of persuasive language and rhetorical devices
- Clear and logical presentation of arguments
About The Author







