Understanding Iron Price Per Metric Ton: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to the iron industry, the price per metric ton is a crucial factor that influences various aspects, from production costs to market demand. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the factors affecting the iron price per metric ton, its historical trends, and its impact on the global market.
Market Dynamics

The iron price per metric ton is influenced by several market dynamics, including supply and demand, production costs, and global economic conditions.
| Market Dynamics | Description |
|---|---|
| Supply and Demand | The price of iron is primarily driven by the balance between supply and demand. An increase in demand without a corresponding increase in supply can lead to higher prices, while an oversupply can drive prices down. |
| Production Costs | Production costs, including raw materials, labor, and energy, play a significant role in determining the price of iron. Higher production costs can lead to higher prices, while lower costs can result in lower prices. |
| Global Economic Conditions | The global economic environment, including factors like inflation, currency fluctuations, and trade policies, can also impact the iron price per metric ton. |
Historical Trends

Understanding the historical trends of the iron price per metric ton can provide valuable insights into the market’s behavior and potential future movements.
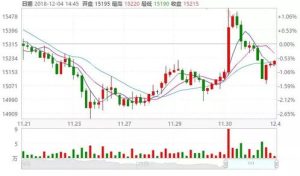
Over the past few decades, the iron price per metric ton has experienced several fluctuations. In the 1990s, the price was relatively stable, hovering around $100 per metric ton. However, in the early 2000s, the price began to rise significantly, reaching a peak of over $400 per metric ton in 2008. Since then, the price has fluctuated, with periods of both highs and lows.
Impact on the Global Market

The iron price per metric ton has a significant impact on various sectors of the global market, including construction, manufacturing, and energy.
In the construction industry, the price of iron is a critical factor in determining the cost of building materials. Higher iron prices can lead to increased construction costs, which can, in turn, affect the overall cost of housing and infrastructure projects.
In the manufacturing sector, iron is a key component in the production of steel, which is used in a wide range of products, from cars to appliances. Fluctuations in the iron price can directly impact the cost of production and, consequently, the prices of consumer goods.
In the energy sector, iron is used in the production of turbines and generators, which are essential components of power plants. Changes in the iron price can affect the cost of generating electricity, which can have a ripple effect on energy prices for consumers and businesses.
Regional Variations
The iron price per metric ton can vary significantly across different regions, depending on factors such as local supply and demand, production costs, and trade policies.
For example, China, the world’s largest producer and consumer of iron, has a significant impact on the global iron price. The country’s policies, such as production quotas and export restrictions, can influence the supply and, consequently, the price of iron.
Conclusion
Understanding the iron price per metric ton is essential for anyone involved in the iron industry or its related sectors. By considering the various factors that influence the price, including market dynamics, historical trends, and regional variations, stakeholders can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the global iron market.