Tone-Loc: A Comprehensive Guide to Tone Mapping Technology
Have you ever wondered about the “Local Tone Mapping” feature that many digital cameras and smartphones now come with? This technology, which is a subset of the broader Tone Mapping process, plays a crucial role in enhancing the imaging experience. Let’s delve into what Tone Mapping is, how it works, and the impact it has on your images.
Understanding Tone Mapping

Tone Mapping is a technique used to compress the dynamic range of High Dynamic Range (HDR) images to a level that can be displayed on standard, low-dynamic range devices like your computer screen or smartphone. The primary goal is to retain as much detail, color, and contrast as possible from the original HDR image while avoiding artifacts like halos, gradient reversals, color distortion, and edge blurring.
Imagine a scene with both bright and dark areas, like a sunset. A standard camera might capture the details of the sky but fail to capture the details of the foreground, which is too dark. Conversely, the foreground might be well-exposed, but the sky appears washed out. Tone Mapping helps to balance these extremes, ensuring that both the sky and the foreground are visible and detailed.
Global vs. Local Tone Mapping
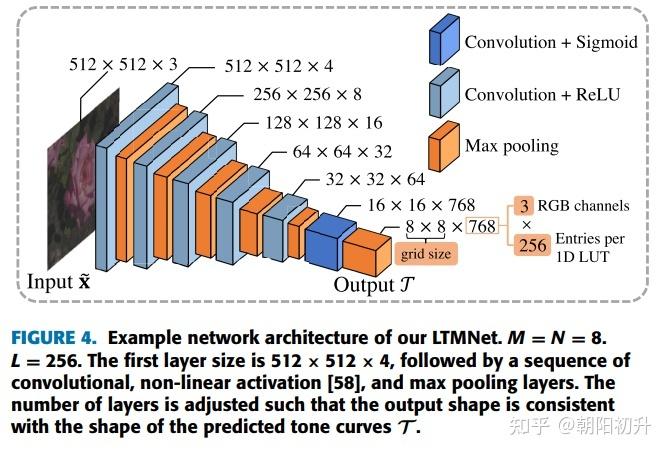
There are two main types of Tone Mapping algorithms: Global Tone Mapping and Local Tone Mapping.
Global Tone Mapping treats the entire image as a single entity, applying the same adjustments to all pixels. This method is computationally efficient and can prevent artifacts like halos and gradient reversals. However, it may also result in a loss of detail, especially in areas with high contrast or in the highlights and shadows.
Local Tone Mapping, on the other hand, takes into account the spatial distribution of pixels. It adjusts the tone mapping based on the local brightness and contrast of each pixel. This method can preserve more detail and texture, especially in complex scenes with varying lighting conditions. However, it can be more computationally intensive and may still produce artifacts in some cases.
How Tone Mapping Works
The process of Tone Mapping involves several steps:
-
Exposure Fusion: This step combines multiple images taken at different exposures to create an HDR image. The goal is to capture the full range of brightness and contrast in the scene.
-
Dynamic Range Compression: This step compresses the dynamic range of the HDR image to a level that can be displayed on standard devices. This is done by mapping the brightness values of the HDR image to a smaller range of values that can be displayed on the screen.
-
Color Correction: This step adjusts the colors of the image to ensure that they look natural and accurate on the screen.
The Impact of Tone Mapping
The impact of Tone Mapping on your images can be significant:
-
Better Detail: Tone Mapping can help to preserve details in both the highlights and shadows of an image, resulting in a more realistic and vibrant image.
-
Improved Contrast: Tone Mapping can enhance the contrast of an image, making it more visually appealing.
-
Reduced Artifacts: Tone Mapping can help to reduce artifacts like halos and gradient reversals, resulting in a cleaner and more natural image.