What Does Tone Mean in Literature?
The term “tone” in literature refers to the attitude or mood conveyed by a writer through their choice of words, syntax, and overall style. It is a crucial element that can greatly influence how readers perceive and interpret a piece of writing. Understanding the tone of a literary work allows readers to delve deeper into the author’s intentions and the underlying themes. In this article, we will explore the various dimensions of tone in literature, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its significance and application.
Defining Tone
At its core, tone is the emotional atmosphere or mood that a writer creates in a literary work. It can range from serious and solemn to humorous and light-hearted. The tone is often conveyed through the writer’s choice of vocabulary, sentence structure, and the overall style of the text. For instance, a novel with a dark and brooding tone may use words like “melancholic,” “dismal,” and “forlorn,” while a comedy might employ words like “jovial,” “witty,” and “playful.” The tone sets the stage for the reader’s emotional response and can shape their interpretation of the story.
Types of Tone

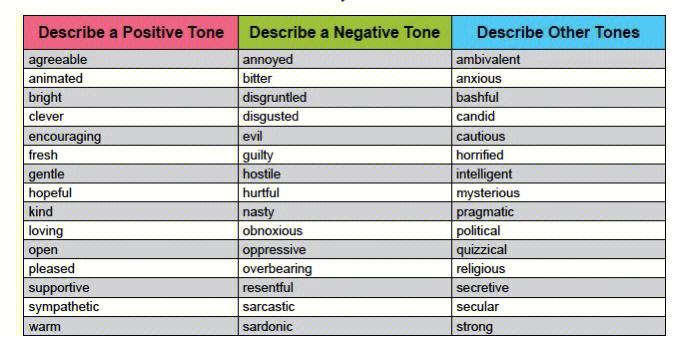
There are several types of tone that can be found in literature, each with its own unique characteristics. Here are some of the most common ones:
| Type of Tone | Description |
|---|---|
| Humorous | Conveys amusement, wit, or sarcasm. Often used in comedies or satirical works. |
| Ironical | Expresses a contrast between what is said and what is meant. Often used to highlight absurdity or hypocrisy. |
| Tragic | Conveys a sense of sorrow, despair, or loss. Often used in鎮插墽鏂囧. |
| Optimistic | Expresses hope, confidence, or a positive outlook. Often used in works that focus on growth and progress. |
| Dark | Conveys a sense of gloom, despair, or dread. Often used in works that explore the darker aspects of human nature. |
Creating Tone

Creating the right tone in a literary work is a delicate balance that requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key elements that contribute to the development of tone:
-
Vocabulary: The choice of words can greatly impact the tone of a piece. Using specific adjectives, nouns, and verbs can evoke certain emotions and set the desired mood.
-
Sentence Structure: The length and complexity of sentences can also contribute to the tone. Short, choppy sentences can create a sense of urgency or tension, while longer, more complex sentences can convey a sense of depth and introspection.
-
Point of View: The perspective from which a story is told can influence the tone. First-person narratives often have a more intimate and personal tone, while third-person narratives can offer a broader perspective and a more objective tone.
-
Setting: The time and place in which a story unfolds can also contribute to the tone. A modern urban setting might convey a sense of realism and urgency, while a historical setting might evoke a sense of nostalgia and reflection.
Significance of Tone
The tone of a literary work plays a crucial role in shaping the reader’s experience and interpretation. Here are some of the key reasons why tone is significant:
-
Emotional Connection: The tone can evoke emotions in the reader, allowing them to connect with the characters and the story on a deeper level.
-
Understanding Themes: The tone can help readers understand the underlying themes of a work. For example, a dark and brooding tone might suggest a focus on the human condition and the complexities of life.
-
Creating Atmosphere: The tone can set the stage for the reader’s imagination, creating a vivid and immersive experience.
-
Reflecting Character: The tone can reflect the character’s emotions and personality, providing insight into their inner world.
About The Author